Hildegarde de Bingen , je n’ai pas pris le temps de faire des recherches sur le net pour m’en assurer, fut réellement une sainte du XIe siècle qui rédigea une encyclopédie nommée Physica. Permettez alors que je m’adresse aux végétaux amorphes que sont les étudiants en lettres, en général, et ceux qui font leurs humanités en particulier (bien qu’ils ignorent totalement ce que cela signifie). Physica n’a rien à voir avec un groupe de cette musique dépravée que vous nommez Tektonik. En grec, phûsis signifie la nature. Donc Physica, ce sont les choses de la nature, quoi. Pardonnez-moi, je vieillis, je ne supporte plus les jeunes…
Et puisque l’on s’entretenait de plantes, Hildegarde en avait découvert une fameuse. Non, Victor, elle ne se fume pas, n’insiste pas. En fait, nombre de laboratoires pharmaceutiques aimeraient mettre la main dessus, et sur ses molécules plus précisément. Les labos, et d’autres, hein. Il leur faut donc mettre la main en premier lieu sur le livre Physica d’Hildegarde. Et pour ce faire, d’ailleurs, on n’hésite pas une seconde à assassiner violemment des bibliothécaires… Américaines, certes, mais tout de même.
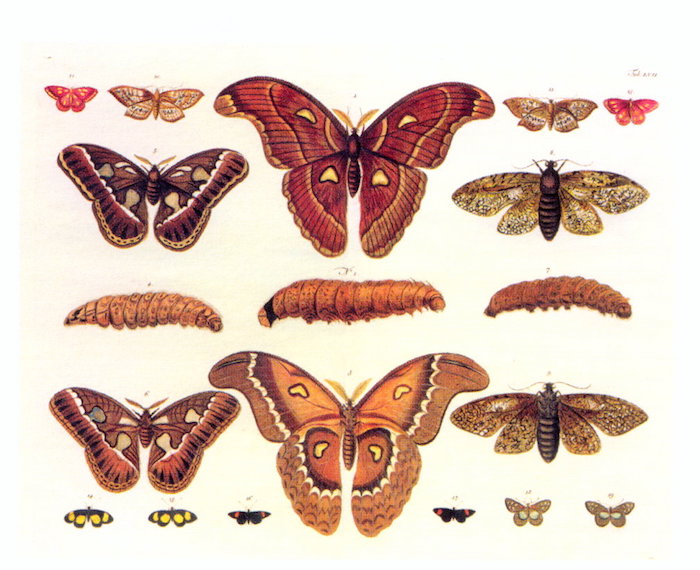
Laurette, elle, travaille au Museum d’histoire naturelle de Paris. Dans sa prochaine exposition, elle brûle de révéler au public l’existence de cette plante, certes, mais surtout de pouvoir en exposer un spécimen. La voici donc empêtrée dans une affaire de botanique et de rangement alphabétique. Car Hildegarde, comme si elle l’avait senti, a planqué les références de ses plantes dans les méandres d’un idiome complexe : la lingua ignota. Même à l’attention des non-latinistes, je n’ose traduire.
Retrouver l’exemplaire du Physica sera essentiel, mais ce dernier aura pas mal bourlingué depuis sa rédaction, se passant de mains en mains, parcourant l’Europe, et finalement pour peu que l’on sache où il se terre, il manquerait justement les passages qui suscitent tant d’enthousiasme. C’est que le marché du livre ancien draine son lot de crapules prêtes à toutes les basses pour s’emparer d’une denrée précieuse.
Aussi, au fil de son enquête à la façon de Miss Marple, elle côtoiera plusieurs personnages historiques qui ont croisé le chemin d’Hildegarde, ou de son livre. Elle parcourt les siècles, suivant un fil d’Ariane ténu et fragile, pour retrouver enfin le saint Graal botanique. Point commun à chacun ? Un goût prononcé pour la classification, le rangement et la mise au point d’une méthode de classement qui élabore finalement les fondements d’une science de l’information et de la documentation.
Or, tout cela est beau, se dit Dieu, mais franchement, n’est pas un peu cantonné aux spécialistes. Eh, bien, Seigneur, je trouve que vous jugez un peu à l’emporte-pièce. D’abord, ce roman est tout bonnement passionnant. Et ce n’est rien de le dire. Si son thème peut rebuter de prime abord, il faut au contraire passer outre et se lancer aux côtés de Laurette, à corps perdu, dans une aventure riche et dynamique. Quoiqu’un peu à l’eau de rose, de temps en temps. Désolé Sylvie, mais comprends ma position d’homme, c’est vrai que cette liaison, même justifiée et intégrée à ton histoire, elle est vécue un peu gnangnan…
Pour autant, Seigneur, vous n’avez pas tout à fait tort. En ce sens que le livre devient épuisant de par cet aller-retour permanent entre passé et présent. La foule d’information provenant du passé, et chargée d’illustrer le présent devient un peu écrasante, et l’on décroche – particulièrement le passage en Belgique, vraiment peu passionnant – sans une volonté de fer. Ou des insomnies chroniques. La table des matières est un roman épuisant. On en sort ravi et séduit pas ce style peu commun, autant que vidé de son énergie par le tour de force qu’il représente.
L’intrigue se poursuit avec son accumulation de détails, d’indices, qui nous poussent à spéculer sur les intentions de tel ou tel, les implications de l’un ou l’autre qui croiseraient les intérêts d’untel… Bref, on suit, non sans peine parfois, mais on palpite.
Après… je ne cache pas qu’en dépit de toutes ses qualités, le roman offre une accroche prenante, mais réclame une attention régulière. Et surtout, de ne pas s’arrêter en plein milieu d’un passage rétrospectif, et de reprendre trop longtemps après, sous peine de se refaire ledit passage. Comme la plume agile nous séduit, on se laisse porter. Et l’on parcourt nous aussi les jardins où l’on dénichera la plante mystique qui offre l’immortalité…
D’ailleurs, je vais m’acheter une pelle de ce pas.






















-dccd31ff-7a7a-4827-b605-79504f84bdc1.png)



